Glimpsing the Green Future
Here we are, halfway through 2025, and it feels like we’re standing at a bit of a crossroads. On one hand, renewable energy’s flying high in the UK. On the other, there’s still plenty of oil and gas keeping the lights on. So the question is: what’s the real picture today? And more to the point—what will it look like ten years from now?
In this article, we’ll break down exactly how much of the UK’s energy is coming from green sources in 2025, who’s pulling their weight (and who isn’t), and what 2035 might bring. Expect numbers, predictions, a bit of opinion, and hopefully, a sense of what we’re actually headed for.
Where We Stand in 2025: Is the UK Truly Going Green?
Current Renewable Share in the National Mix
As it stands, about 47% of the UK’s electricity comes from renewable sources. That figure includes wind, solar, hydro, and bioenergy. Fossil fuels still make up just under 40%, while nuclear covers roughly 15%.
Here’s what that breakdown looks like:
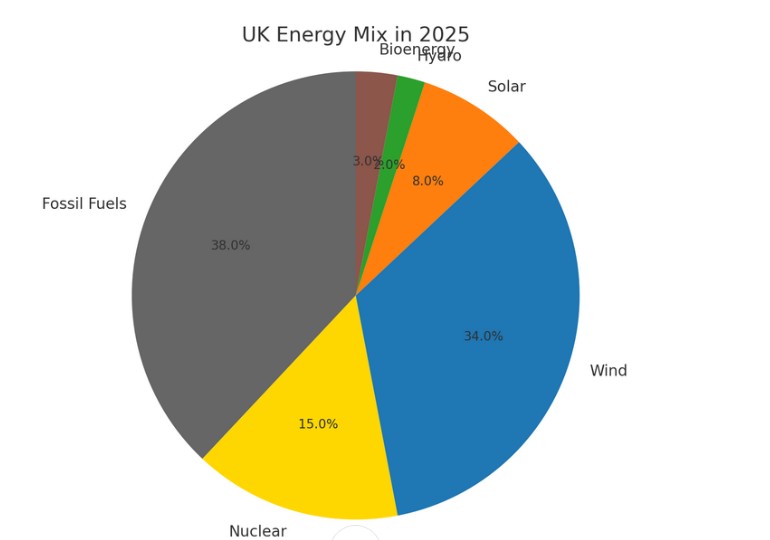
This isn’t bad progress, considering that just a decade ago, fossil fuels held over 70% of the share. But electricity is only part of the story. Heating, transport, and industrial energy still rely heavily on gas, petrol, and diesel.
Who’s Powering Us? The Main Players in 2025
Wind power is currently the heavyweight, generating around 34% of the UK’s electricity—most of it offshore. It’s clean, consistent, and the North Sea’s become a proper goldmine of spinning turbines.
Solar power is growing, but still trails behind at about 8%. Seasonal variability and planning resistance hold it back, especially in England.
Bioenergy (which includes biogas, landfill gas, biomass, and transport biofuels like ethanol and biodiesel) provides a modest but growing 3%. Not headline-grabbing, but absolutely vital in transport and industrial use.
Hydro sits around 2% and likely won’t change much—it’s limited by geography.
Nuclear isn’t renewable, but it’s low-carbon and still covers 15%, mainly from ageing reactors.
Challenges and Setbacks
Despite all the green chatter, there are issues. Offshore wind has seen supply chain delays and rising costs. Solar farms spark debates over land use, especially in farming regions. Biofuel adoption remains sluggish, especially in HGV fleets. And hydrogen? Let’s just say it’s still more theory than practice.
The Forecast for 2035: What the Experts Expect
Government Goals vs Reality
The UK government’s aiming for a net-zero power grid by 2035. That means no fossil fuels unless their emissions are fully captured. On paper, it’s achievable. In practice, it’ll take serious investment and a bit of luck.
According to the Climate Change Committee and National Grid ESO, we’ll need to double our low-carbon capacity in ten years. That means more wind, more solar, a new approach to heating, and serious innovation in transport fuels.
Wind Power: Still King of the Hill?
Wind will likely stay at the top, projected to make up around 40% of the energy mix by 2035. Several large-scale projects in the Dogger Bank and Hornsea zones will come online by then, supported by better grid infrastructure and smarter storage tech.
Floating turbines could even unlock deeper waters off the Scottish coast, opening up new wind corridors.
Solar: Sleeping Giant or Oversold Promise?
Solar power is expected to more than double, rising from 15GW today to around 40GW in 2035.
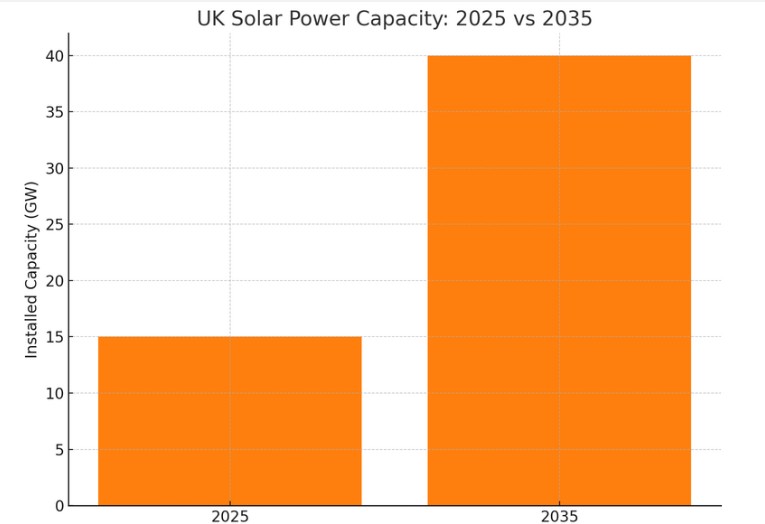
This growth will rely heavily on domestic rooftop installations and clever integration with home batteries and heat pumps. Solar won’t ever be our main source, but in combination with storage, it’ll punch well above its weight.
Bioenergy and Green Fuels: Niche or Necessary?
Here’s where things get divisive. Some experts see bioenergy as a bridging fuel, helping decarbonise sectors like aviation and heavy industry. Others call it inefficient and land-intensive.
Still, green fuels—including advanced ethanol, biodiesel, and synthetic fuels—are expected to provide 10% of energy needs by 2035. Their role in decarbonising older vehicles, planes, and ships will be key.
Biogas from food waste and slurry will also help power combined heat and power systems across rural areas.
Green Hydrogen: Breakthrough or Buzzword?
Hydrogen’s been hyped for years, but mid-2025 still sees more talk than delivery. By 2035, that could change.
Expect 8% of the energy mix to come from hydrogen, mainly powering industrial furnaces, backup power stations, and perhaps heavy transport. But large-scale rollout depends on cheap electrolysers and lots of surplus renewable electricity.
What Will the 2035 Energy Mix Look Like?
Let’s stack it up visually.
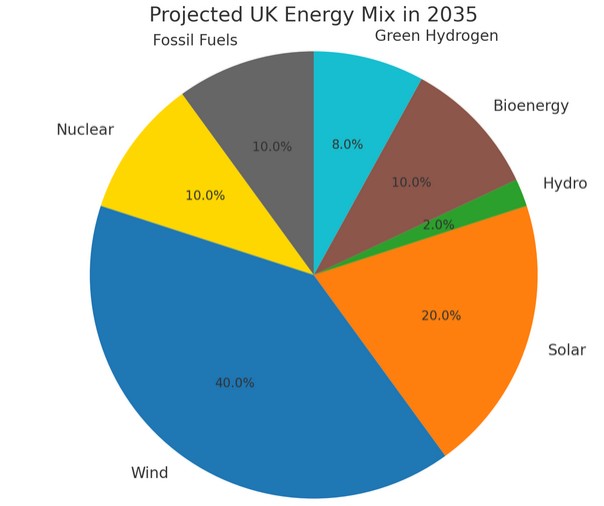
The new mix could look like this:
- Wind: 40%
- Solar: 20%
- Bioenergy: 10%
- Green Hydrogen: 8%
- Nuclear: 10%
- Hydro: 2%
- Fossil Fuels (with CCS): 10%
It’s worth noting that even with a big push, fossil fuels won’t disappear entirely—but they’ll be cleaner or offset by carbon capture. That’s the compromise built into most forecasts.
The Transport and Heating Question
By 2035, most new cars will be electric. Home heating is shifting towards heat pumps, though retrofitting old housing stock remains expensive and messy.
This all adds pressure to the electricity grid. Can renewables carry the extra weight? If rollout keeps pace, yes. But if we fall behind, there’s a risk of shortfalls—especially in winter.
Winners, Losers, and Big Questions Ahead
Who Stands to Benefit the Most?
If things go to plan, the green sector could add tens of thousands of jobs—especially in wind engineering, solar installation, and hydrogen development. Coastal towns and ex-industrial areas could see a real revival.
The biggest winners will be those who invest early, upskill fast, and focus on flexible, localised energy solutions.
What Might Stall Progress?
Here are five major risk factors:
- Planning delays – NIMBY resistance is slowing wind and solar approvals.
- Supply chain gaps – We still rely heavily on imported materials for renewables.
- Political wobbles – A change in government priorities could shift funding.
- Grid limitations – Upgrades to infrastructure are slow and costly.
- Public confusion – Misinformation and resistance to lifestyle changes might limit adoption.
Final Thoughts: The 2035 Snapshot in Perspective
Will we look back in 2035 and see a green energy success story? I think we might—if we keep moving. The UK’s got the brains, the tech, and the wind in its sails. But we’ll need clear policies, serious funding, and public backing to stay on course.
One thing’s for sure: energy in 2035 won’t look like it does today. Whether that’s something to celebrate or worry about… well, that’s up to us.
…


